Definition
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that occur in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products.
Expanded Explanation
Cellular respiration involves breaking down glucose molecules (and sometimes fats and proteins) to produce ATP, the main energy currency for cells. This process allows cells to harness the energy stored in glucose and other nutrients and use it to perform their functions.
Importance
Cellular respiration is a fundamental process in biology, as it provides the energy necessary for the survival of cells and, consequently, living organisms. Without cellular respiration, most life forms would be unable to extract energy from their food and would cease to exist.
Context and Usage
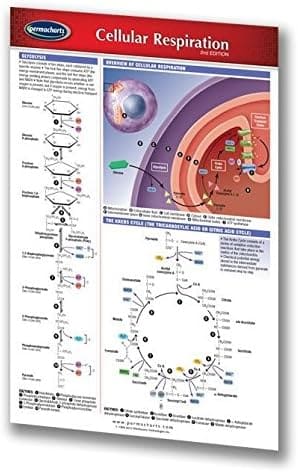
In the field of biology, the term “cellular respiration” is used to describe the process through which cells obtain energy. There are three main stages of cellular respiration: Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain, each occurring in a specific region of the cell.
Examples
- Example 1: Human muscle cells perform cellular respiration to produce the ATP needed for muscle contraction.
- Example 2: Plant cells undergo cellular respiration at night, using the glucose produced during photosynthesis to generate ATP.
Understanding Cellular Respiration
A common misconception is that only animal cells perform cellular respiration. In fact, all eukaryotic cells, including plant and fungi cells, perform cellular respiration to generate ATP.
Related Glossary Terms
- Glycolysis: This is the first stage of cellular respiration, where glucose is broken down in the cytoplasm of the cell.
- ATP (adenosine triphosphate): This molecule is the main energy carrier in cells and is produced during cellular respiration.
Visual and Reading Aids
External Resources
Related Articles
- From Food to Energy: The Cellular Respiration Aerobic Process: This article is a comprehensive blog post that delves into the biological mechanisms that transform the food we consume into usable energy through the process of aerobic cellular respiration.
- Cellular Respiration ATP: Why and What Foods Are Better?: This is a blog post that delves into the essential process of cellular respiration, the role of ATP, and how certain foods can optimize this process for better health and energy levels.