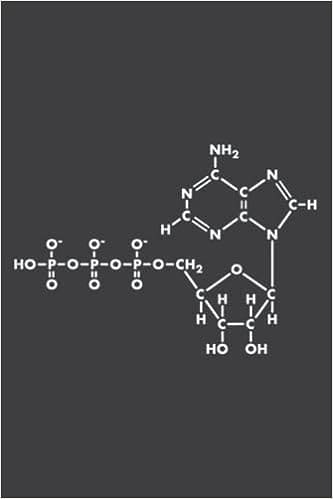
Definition
ATP, short for adenosine triphosphate, is a complex organic chemical that fuels numerous processes in living cells. These processes include muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis.
Expanded Explanation
We often refer to ATP as the “energy currency” of the cell, acting as a potential energy storage. Transitioning to the process of hydrolysis, breaking down an ATP molecule releases energy. This released energy is then harnessed to drive endergonic reactions within cells.
Importance
ATP is fundamental to life because it provides the energy needed for a variety of cellular processes. It’s vital for movement, cell division, protein synthesis, and transmitting nerve impulses, among many other functions. Without ATP, life as we know it would not exist.
Context and Usage
ATP is used in the context of cellular biology and biochemistry. ATP is frequently mentioned in discussions about cellular respiration. This process involves cells converting biochemical energy from nutrients into ATP, followed by the release of waste products.
Examples
- Example 1: In muscle cells, ATP is required for muscle contraction. It provides the energy for the proteins in the muscle to contract and enables movement.
- Example 2: ATP also plays a crucial role in the brain. It provides the energy for nerve cells to transmit signals, playing a vital role in brain function and cognition.
Understanding ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
A common misconception about ATP is that it’s the only form of energy in the cell. While it’s a primary energy source, cells also use other molecules like NADH and FADH2 to store and transfer energy.
Related Glossary Terms
- ADP (Adenosine diphosphate): ADP is the product left after the energy stored in an ATP molecule is released. It can be converted back to ATP in the mitochondria of cells.
- Cellular Respiration: This is the process by which cells produce ATP from nutrients.
Visual and Reading Aids
External Resources
Related Articles
- Unlocking Triphosphate Adenosine: The Incredible Energy Currency of Life: This blog post offers a deep dive into the crucial role of ATP, the primary energy carrier in living organisms, and its importance in biological processes.
- Unlocking the Secrets: Understanding the Metabolic Rate of Alcohol: This article explains how ATP is involved in metabolizing alcohol.